

Cohen presented an extensive review of the conditions in which "Robin malformation complex" can occur along with data useful for diagnoses of patients with cleft lips and/or palates and associated anomalies. The characteristic U-shaped CP of PR individuals, distinct from the more common V-shaped CP, was proposed to have developmental and clinical significance, as well as providing strong support for the proposed etiopathogenetic mechanism involving a small and retropositioned mandible that keeps the tongue high in the nasopharynx, preventing the rotation, medial growth, and fusion of the palatal shelves. Hanson and Smith hypothesized the primary pathogenic mechanism of "Robin anomalad" to be early mandibular hypoplasia with secondary posterior displacement and interposition of the tongue between the closing palatal shelves. Anomalad denotes a pattern of morphologic defects that stem from a single, localized, structural anomaly resulting in a cascade of consequent defects, so the term implies a sequence of developmental consequences of a primary defect. Anomalad signifies an etiologically nonspecific complex that can occur as a component of various genetic or teratogenic syndromes of known cause, syndromes of unknown etiology, or as an isolated symptom complex secondary to positional deformation or disruption. In the 1970s, the term Pierre Robin anomalad was introduced, with the implication that the condition was not a specifically delineated syndrome. The condition was known as Pierre Robin syndrome for nearly 50 years before it was understood that multiple etiologies could underlie the same clinical findings, which did not fit with the prevailing definition of a syndrome: a combination of symptoms resulting from a single cause. Natal teeth were associated with one PR patient in a cohort of infants born at Foothills Provincial Hospital in Calgary, Canada, between 19. Through the 1960s, clinicians noted that PR generally occurred without other significant birth defects, although the case of a two-month-old male infant with PR and severe bilateral congenital glaucoma indicated ocular involvement in some affected individuals.

Robin linked the respiratory problems in these children to their physical and psychological development, and indicated that infants with severe retrognathia rarely survive beyond 18 months of age. He also introduced the association of these anomalies with CP. These conditions ultimately result in "physical backwardness" in infancy that persists into adulthood. Robin considered acquired or congenital glossoptosis as a consequence of a small mandible leading to respiratory problems. Following his widely read contribution to the literature on micrognathia in newborns, this triad became known as Pierre Robin syndrome by clinicians.
#Pierre robin sequence vs treacher collins series
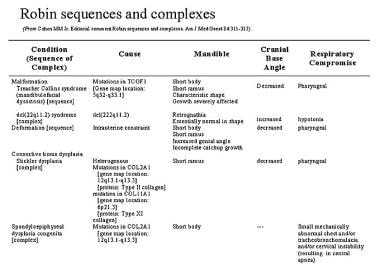
Stomatologist Pierre Robin published an article in 1923 describing a triad of clinical findings in a series of patients, namely, micrognathia, glossoptosis, and obstruction of the upper airways. When mandibular dysmorphology occurs with glossoptosis, respiratory obstruction, and in some cases, a CP, the condition is referred to as Pierre Robin (PR), a term we adopt here. Thus, micrognathia and retrognathia, while providing similar facial profiles, are produced by different primary developmental processes, and each may integrate differently with tongue and palatal development. Micrognathia describes a mandible that is absolutely reduced in size, indicating that the mandible is primarily affected, while retrognathia refers to a normally sized mandible that is placed posteriorly relative to the upper jaw. Micro- and retrognathia are the most common terms used to describe mandibular phenotypes in mandibulofacial dysostosis, yet the current lack of precision in usage of these terms in diagnoses of mandibular dysmorphology does not critically consider the potentially distinct etiology of these phenotypes and their influence on the possible sequelae of anomalies. Since being named for the physician who provided an early description, it was variously defined as a set of anomalies that can include micro- or retrognathia, glossoptosis, respiratory obstruction, and cleft palate (CP), and termed Pierre Robin syndrome, sequence, anomalad, or complex. Pierre Robin is an ill-defined disorder with specific mandibulofacial involvement that continues to defy a consistent definition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
